Introduction
Scandium oxide (Sc2O3) is a rare and valuable material with unique properties. It plays a crucial role in advanced technologies, especially in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). SOFCs are important for creating clean energy by converting chemical energy into electricity with high efficiency and low pollution. Scandium oxide helps make these cells more efficient and longer-lasting.
What is Scandium Oxide?
Scandium oxide is a compound made from scandium, a rare earth element. It looks like a white powder and does not have a smell. Scandium oxide can handle very high temperatures without breaking down, which is essential for many high-temperature uses, like in fuel cells. It also allows ions to move through it easily, which is crucial for fuel cells that need the movement of ions to generate electricity.
What Are Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs)?
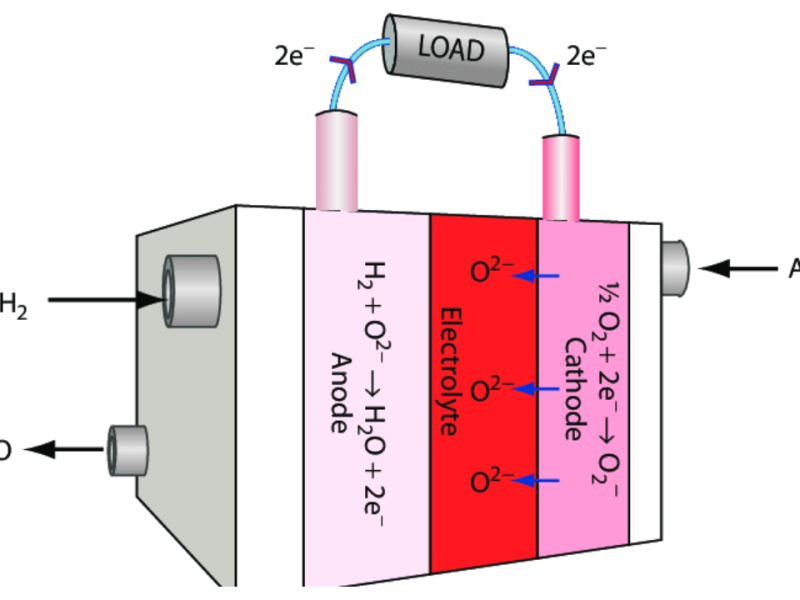
SOFCs are a type of fuel cell that works at high temperatures, usually between 600°C and 1,000°C. They use a solid ceramic material as the electrolyte, which is the part that conducts ions. The high temperature allows SOFCs to use many types of fuels, such as natural gas, hydrogen, and biofuels. Because of the heat, SOFCs are very efficient, turning up to 60% of the fuel’s energy into electricity. This makes them a great option for power generation and transport.
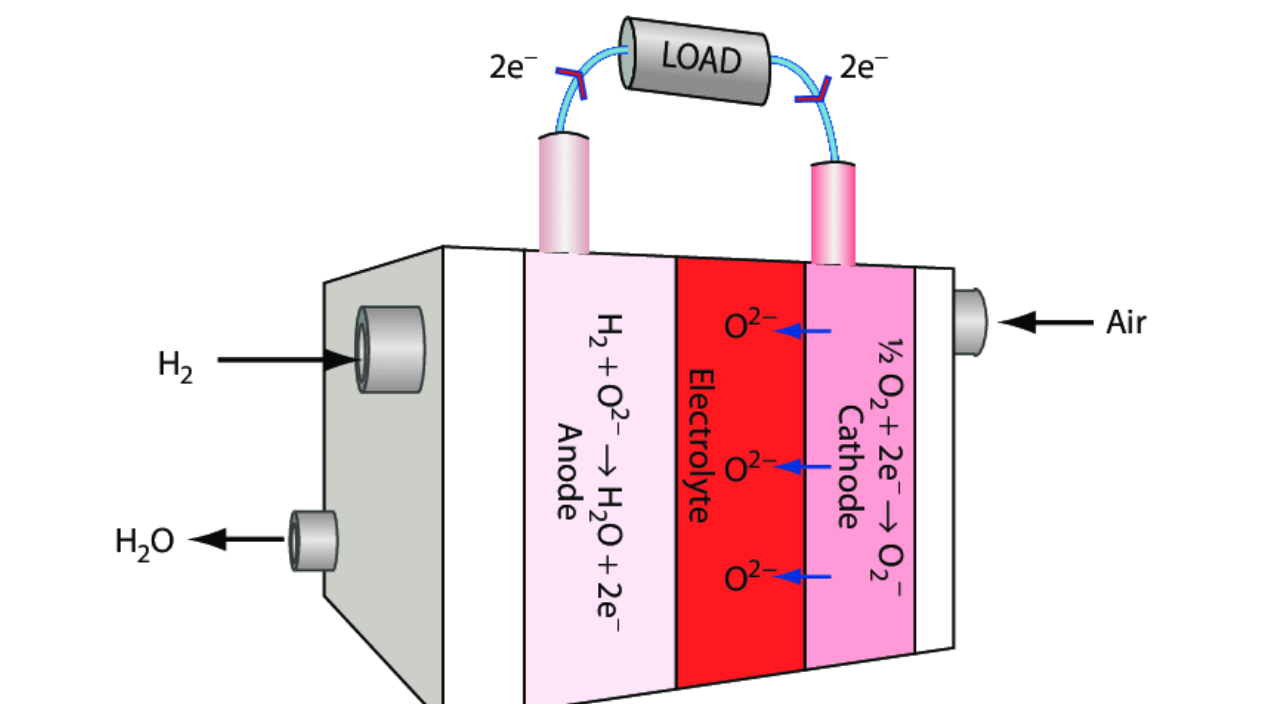
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Image by: ResearchGate.
Why is Scandium Oxide Important for SOFCs?
- Improves Ionic Conductivity: Scandium oxide makes the electrolyte in SOFCs work better. The electrolyte is the part that helps ions move between the two sides of the cell. For SOFCs to work efficiently, the electrolyte needs to let ions pass through it easily. Adding scandium oxide helps boost this conductivity, improving the fuel cell’s performance.
- Increases Durability: SOFCs operate at very high temperatures, which can cause damage to materials over time. Scandium oxide helps stabilize the parts of the fuel cell, making them more resistant to heat and mechanical stress. This means the fuel cell lasts longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering costs.
- Lowers Operating Temperature: Traditional SOFCs often need to operate above 900°C, which can limit their use and increase costs. With scandium oxide, the fuel cell can work at lower temperatures, around 600°C to 800°C. Lower temperatures mean less wear on the materials, a longer lifespan, and reduced costs for insulation and cooling.
Applications of Scandium Oxide in SOFCs
- Stationary Power Generation: Scandium oxide-enhanced SOFCs are perfect for stationary power generation, such as power plants, backup systems, and distributed energy. Their high efficiency and durability make them a reliable source of clean energy, especially in remote areas or where a steady power supply is critical.
- Transportation: Scandium oxide SOFCs are also useful in the transportation sector. They can power vehicles where long-range and low emissions are essential. For example, they are being tested in trucks, ships, and even planes. Their ability to use different fuels makes them flexible for various transport needs.
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: In CHP systems, SOFCs generate electricity and use leftover heat for heating. This dual use of energy boosts overall efficiency to about 85%. Scandium oxide improves the performance and durability of these systems, making them more attractive for homes, businesses, and factories.
Future Potential of Scandium Oxide in SOFCs
The future of scandium oxide in SOFCs is promising. As the need for clean energy grows, so does the demand for efficient and reliable fuel cells. Ongoing research aims to enhance scandium oxide’s properties, making it even more effective in fuel cells. Advances in production methods may also help reduce costs, making scandium oxide more accessible.
Challenges and Opportunities
One main challenge is the high cost of scandium oxide. Scandium is rare, and its extraction is costly. However, new scandium sources and improved extraction methods could lower the price. Additionally, the benefits, such as increased efficiency and durability, can make it a worthwhile investment despite higher initial costs.
There are also opportunities for new uses. As scandium oxide-enhanced SOFCs prove valuable in power generation and transport, other sectors, like portable electronics or off-grid systems, may adopt this technology.
Conclusion
Scandium oxide is vital for next-generation solid oxide fuel cells. It improves conductivity, increases durability, and reduces operating temperatures, making it essential for enhancing SOFC performance. While cost challenges exist, the potential benefits are significant. As research continues and costs drop, scandium oxide could become a key player in the future of clean energy.
